Loading.....
Why SQL Proficiency is Essential for Database Testing

In today's technology-driven world, database testing is crucial for ensuring the reliability and functionality of software applications. SQL (Structured Query Language) is a fundamental tool for testers working with databases, enabling them to validate data integrity, verify application functionality, and ensure overall system performance. Let's delve into the world of SQL for database testing in this comprehensive guide.
What is SQL for Testers?
SQL, or Structured Query Language, is a specialized programming language used for managing and manipulating relational databases. For testers, SQL serves as a powerful tool for querying databases, retrieving data, performing data manipulation operations, and validating database functionality.
Why Should You Learn SQL?
SQL serves as the lingua franca for interacting with relational databases. It provides a standardized syntax for querying, updating, and managing data stored in a database management system (DBMS). In the context of database testing, SQL empowers testers to:
- Retrieve Test Data: SQL queries facilitate the extraction of test data from the database, allowing testers to create datasets that simulate real-world scenarios and edge cases.
- Verify Data Integrity: Testers can employ SQL to validate the integrity of data by executing queries that compare expected results with actual outcomes, ensuring that the database maintains consistency and accuracy.
- Assess Performance: SQL queries enable performance testing by analyzing query execution times, identifying bottlenecks, and optimizing database performance for enhanced scalability and responsiveness.
- Execute Data Manipulation Operations: Through SQL, testers can perform data manipulation operations such as insertions, updates, and deletions to simulate user interactions and assess the system's behavior under different conditions.
- Regression Testing: As software evolves through updates and modifications, it's essential to ensure that existing functionalities remain intact. SQL queries aid in regression testing by re-executing predefined sets of queries to validate that recent changes haven't introduced any unintended side effects or regressions in the database functionality.
- Security Testing: Database security is a critical concern in today's digital landscape. SQL queries are employed to assess the effectiveness of security measures such as access controls, encryption, and data masking. Testers simulate various security threats by executing queries to exploit vulnerabilities and evaluate the system's resilience against potential attacks.
Skills Required for DB Testers
Effective database testers require a combination of technical and non-technical skills to perform comprehensive database testing. Here are the top five essential skills for aspiring and seasoned database testers:
- SQL Proficiency: Mastery of Structured Query Language (SQL) is paramount for database testers. They must be skilled in writing and executing complex SQL queries to validate data integrity, verify business logic, and uncover potential anomalies within the database schema.
- Database Fundamentals: A comprehensive understanding of database fundamentals is essential, including knowledge of database management systems (DBMS), data modeling concepts, normalization techniques, and transaction management. Proficiency in popular database systems such as MySQL, Oracle, SQL Server, or PostgreSQL is highly desirable.
- Data Analysis Skills: Database testers should possess strong analytical skills to interpret data patterns, identify outliers, and perform root cause analysis of defects. They must be capable of designing and executing data-driven test scenarios to validate the accuracy and completeness of data transformations, aggregations, and calculations
- Test Automation: Automation testing plays a vital role in database testing, enhancing efficiency, coverage, and reliability. Testers should be familiar with automation tools and frameworks tailored for database testing, such as Selenium WebDriver, TestNG, or JUnit. Automating repetitive tasks allows testers to focus on more complex testing scenarios and ensure thorough test coverage.
- Understanding of ETL Processes: Many software applications rely on Extract, Transform, Load (ETL) processes to manage data flow. Database testers should have a deep understanding of ETL workflows, data mapping, and transformation rules to validate the accuracy and integrity of data throughout the ETL pipeline. This includes verifying data consistency, completeness, and correctness during the extraction, transformation, and loading phases.
Essential SQL Commands for Database Testing
To proficiently test databases using SQL (Structured Query Language), testers must acquaint themselves with fundamental SQL commands and constructs. Here are some essential SQL commands commonly used in database testing:
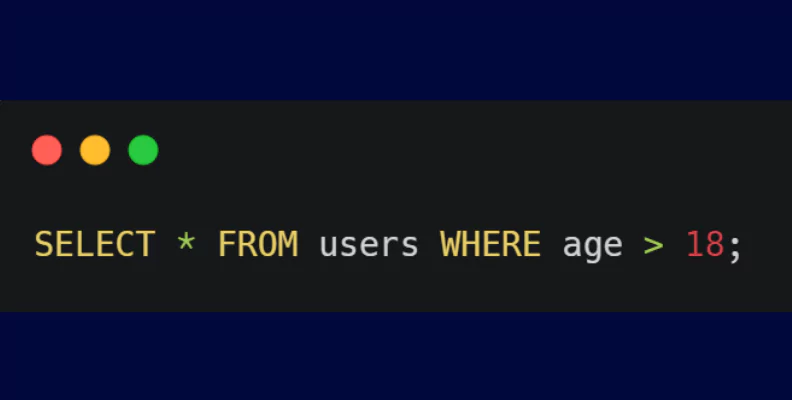
- SELECT: The SELECT statement retrieves data from one or more tables based on specified criteria, allowing testers to fetch relevant data for testing purposes.
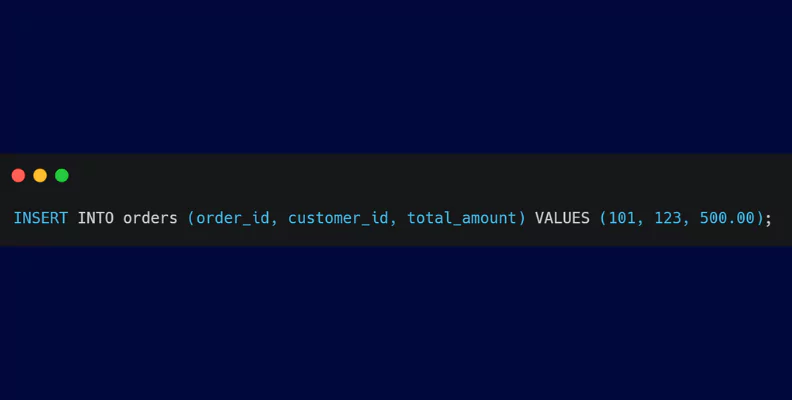
- INSERT: The INSERT statement adds new records to a table, enabling testers to create test data or simulate user interactions.
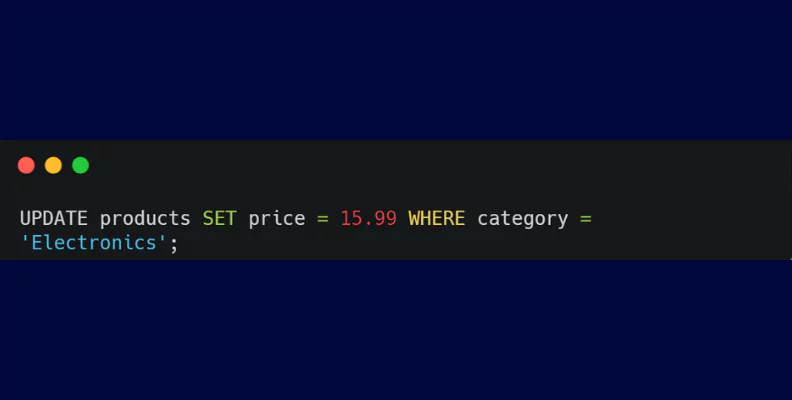
- UPDATE: The UPDATE statement modifies existing records in a table, facilitating the testing of data update functionalities.
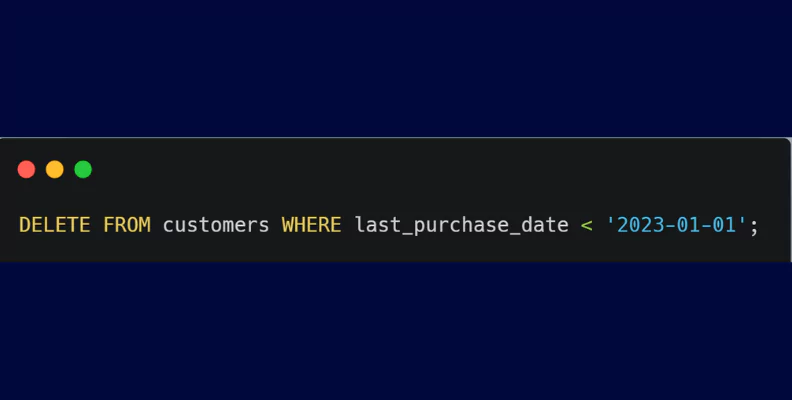
- DELETE: The DELETE statement removes records from a table, allowing testers to validate data deletion operations.
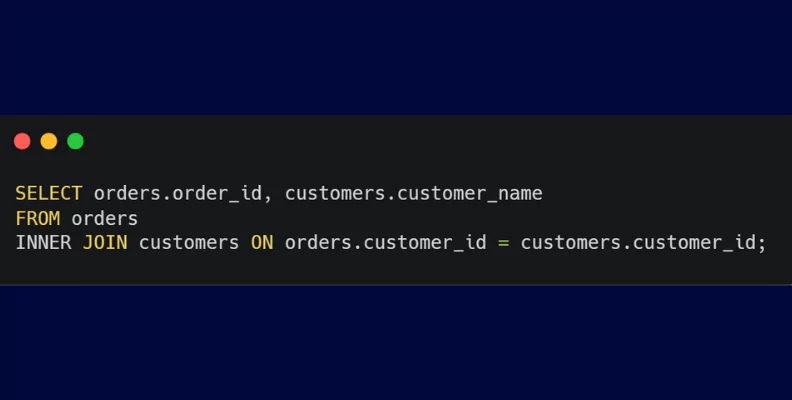
- JOIN: Joins are used to retrieve data from multiple tables based on related columns, essential for testing queries involving data from multiple entities.
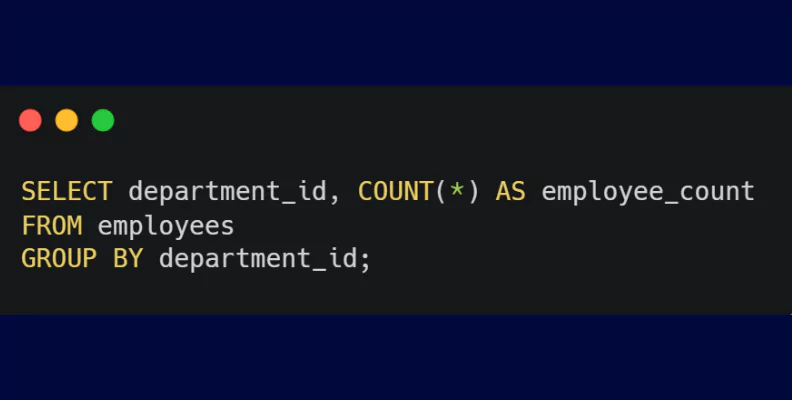
- GROUP BY: The GROUP BY clause is used to group rows that have the same values into summary rows, facilitating aggregation and analysis.
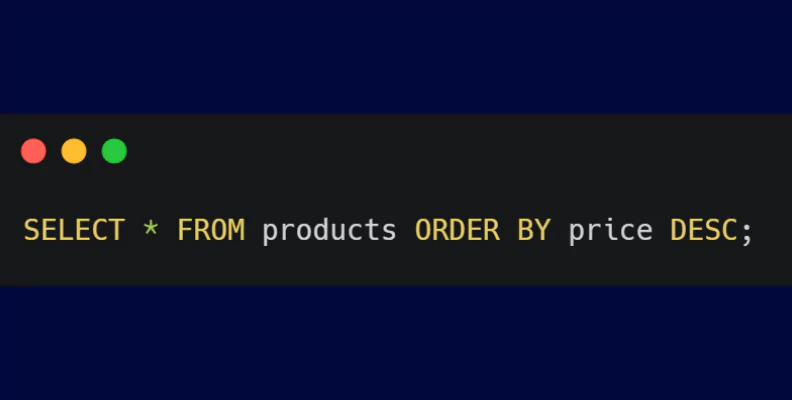
- ORDER BY: The ORDER BY clause sorts the result set in ascending or descending order based on specified columns.
Best Practices for SQL-Based Database Testing
To ensure the effectiveness and efficiency of SQL-based database testing, testers should adhere to the following best practices:
- Use Parameterized Queries: Employ parameterized queries to prevent SQL injection attacks and enhance query reusability and maintainability.
- Optimize Query Performance: Optimize SQL queries by indexing columns, avoiding unnecessary joins, and utilizing query execution plans to enhance database performance.
- Test Edge Cases: Test edge cases and boundary conditions to validate the robustness and resilience of the database under various scenarios.
- Automate Testing Processes: Leverage automation tools and frameworks to streamline database testing, increase test coverage, and accelerate the testing lifecycle.
- Document Test Cases: Document SQL test cases comprehensively, including input data, expected outcomes, and validation criteria, to facilitate collaboration and knowledge sharing among team members.
- Conduct Regression Testing: Perform regression testing regularly to ensure that database changes or updates do not introduce unintended side effects or regressions.
- Collaborate with Developers: Foster collaboration between testers and developers to address database-related issues promptly and iteratively improve database quality.
Conclusion
SQL is an indispensable tool for conducting comprehensive and effective database testing. By mastering SQL commands and adopting best practices, testers can validate data integrity, assess performance, and ensure the reliability of database-driven applications. By embracing SQL-centric testing methodologies, organizations can mitigate risks, enhance software quality, and deliver exceptional user experiences in today's dynamic and competitive digital landscape.
 Back to blog
Back to blog












